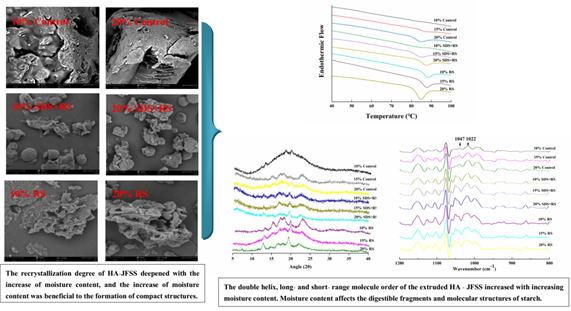
The processing and engineering technology research team of Spice and Beverage Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences has made important progress in the research of deep processing of jackfruit starch. With the help of extrusion technology, the research team systematically studied the changes of water content on the digestibility and molecular structure of high amylose jackfruit starch. The results showed that the water content could significantly affect the digestibility and molecular structure of high amylose jackfruit starch during extrusion. Within a certain water content, reducing the water content could significantly increase the digestibility of starch, and increasing the water content could significantly increase the double helix structure and long-range molecular structure of starch. The microstructure results also confirmed these changes. The above results can provide a theoretical basis for the modification of high amylose starch, especially for the preparation of resistant starch.
Thumbnail of research contents
At present, jackfruit is planted on a large area in Asia, America and the Caribbean at the lowest input cost, with an annual growth rate of more than 15%. The total planting area in the world is more than 4 million mu, and the total planting area of jackfruit in China is more than 500000 mu. Hainan Province and Zhanjiang District of Guangdong Province are the main production areas, with an area of more than 400000 Mu and an annual output of more than 800000 tons. It has become one of the important ways for local farmers to increase their economic income. As a potential commercial starch, jackfruit starch has abundant sources. In recent years, with the increasing investment in research and development, food science and technology workers at home and abroad pay more and more attention to the application fields and development prospects of jackfruit starch.
The fast digested starch, slow digested starch and resistant starch fragments of high amylose jackfruit starch with different water content were prepared by improved extrusion technology. The molecular structure of high amylose starch before and after treatment was analyzed by differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The results showed that the content of slow digested starch and resistant starch decreased significantly (24.08%, 25.99% ~ 17.59%, 16.60%) by reducing water content, indicating that the high amylose jackfruit starch with low water content was easier to digest. Compared with extruded control starch, slow digested starch + resistant starch component and resistant starch sample showed higher gelatinization enthalpy, relative crystallinity and short-range molecular order, but there was no significant difference in gelatinization temperature. In addition, the double helicity, crystallinity and order of extruded control samples, slow digested starch + resistant starch fragments and resistant starch fragments increased with the increase of water content (1.74 J / g, 1.52%, 0.207-9.52 J / g, 32.54%, 0.779). The microstructure and porosity analysis further confirmed the above results, that is, with the increase of water content, the extruded samples changed from a coarser surface structure to a more compact structure. All these results indicate that water content affects the digestible fragments and molecular structure of starch during extrusion. Therefore, it can provide a theoretical basis for the modification of high amylose starch, especially the modification of resistant starch.
The relevant research results were published in the top journal food hydrocolloids, JCR zone I, CATAS, with the title of effects of movement content on digestible fragments and molecular structures of high-altitude pyramid fruit star prepared by improved extraction cooking technology. Zhang Yutong, a Ph.D. student trained by the processing and Engineering Technology Research Office of Spice and Beverage Research Institute , is the first author of the paper, and the leading experts of the team, researcher Tan Lehe, researcher Zhang Yanjun and associate researcher Wu Gang, are the parallel corresponding authors of the paper. This research has been supported by the key R & D plan project of Hainan Province, the central level basic scientific research business fee special project (the project led by Chinese Academy of Sciences) and the cassava industrial technology system (comprehensive test station for coffee, pepper and jackfruit).

Publish research results online
In recent years, Spice and Beverage Research Institute of CATAS has devoted itself to the research of tropical woody grain -- jackfruit starch, and has published 9 SCI papers greater than 5.0 and 4 papers greater than 10.0 in the top journals of international first district such as trends in Food Science & technology, food hydrocolloids, food chemistry, International Journal of biological macromolecules, industrial crops and products, Among them, one article entitled "jackfruit Star: composition, structure, functional properties, modifications and Applications" published in trends in Food Science & technology, an international top journal in the field of food science, was successfully selected into the ESI highly cited paper and was highly praised by experts in the same industry.
Through scientific research in recent years, the processing and engineering technology research team of Spice and Beverage Research Institute of CATAS has clarified the special functional characteristics and molecular structure of jackfruit starch, enriched the starch gel and aging control theory based on starch structure and function cognition, established an efficient preparation method to improve the digestibility and utilization rate of jackfruit starch, and effectively enhanced the influence of tropical food crops in China, It provides an important theoretical reference for the further research and development of functional starch of characteristic tropical crops.