The leisure agriculture research team of South Subtropical Crops Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultrural Sciences has made new progress in the identification of phenolic components and functional activity research of mystic fruit. For the first time, the liquid mass spectrometry (LC-MS) was used to identify the main phenolic substances in Mystic fruit leaves, especially quercetin and myricetin derivatives, and further studied the inhibitory activity of mystic fruit leaves extract on zebrafish angiogenesis, confirming the potential of this extract for cancer development, New potential serum biomarkers for breast cancer were identified by metabolomic analysis. The results showed that the extract from the leaves of mysteria fruit has the potential to be developed as an anti breast cancer drug.
Synsepalum dulcificum belongs to the genus Mysterium. It is famous for its rich mysterin, which can transform sour substances into sweet feelings. In addition to protein, lipid, fiber, carbohydrate, vitamin and other nutritional components, mysterious fruit also contains alkaloids, saponins, flavonoids, polyphenols, cardiac glycosides, anthraquinone and other chemical components. Studies have shown that these phenolic antioxidants have health benefits by inhibiting chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, obesity and diabetes. Natural products are important sources of anticancer drugs and new drug lead compounds. However, due to drug-induced toxicity and drug resistance, its therapeutic effect is limited. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find and develop new cancer therapeutic drugs. The proliferation of cancer cells mainly depends on the surrounding blood vessels to obtain oxygen and nutrients, and tumor metastasis cannot be separated from angiogenesis. However, there are limited reports on elucidating the antiangiogenic and anticancer activities of the extract of mysteria fruit in vivo. Therefore, in this study, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) was used to identify the main phenolic substances in the leaves of mysterious fruit. On this basis, transgenic zebrafish embryos with fluorescent blood vessels were used to evaluate the inhibitory ability of mysterious fruit leaves on angiogenesis. In addition, a mouse model of MCF-7 xenograft tumor was also established to identify potential serum biomarkers of breast cancer, and explore the anti-cancer mechanism of the extract of mysterious fruit leaves by metabolomics.
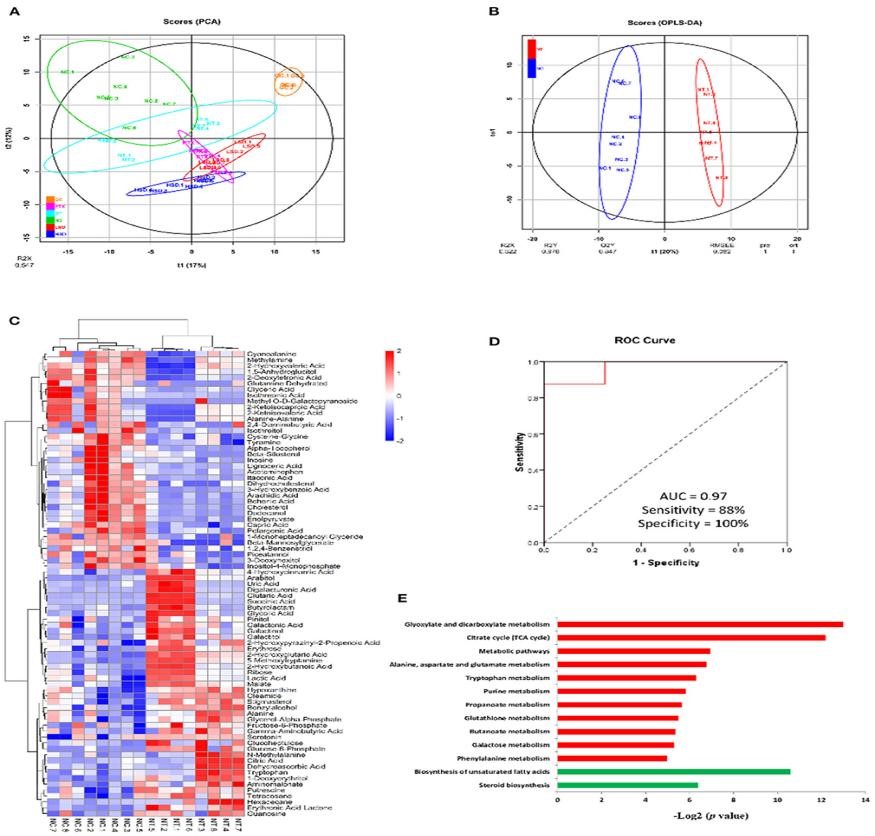
Metabolomic analysis of the serum of MCF-7 xenograft mice treated with the extract of mysteria fruit leaf
The relevant research results were published as "Identification of phenolics from miracle berry (Synsepalum dulcificum) leaf extract and its antiangiogenesis and anticancer activities" in the international academic journal frontiers in nutrition. Ma Feiyue, assistant researcher of South Subtropical Crops Research Institute of CATAS, is the first author, and Zhang Xiumei and Du Liqing are the co authors of the paper. The research was mainly completed in the Key Laboratory of tropical fruit biology of the Ministry of agriculture and rural areas, and was supported by such scientific research projects as the basic business expenses of the central public welfare scientific research institutes, the natural science fund of Hainan Province, and the excellent and rare fruit innovation team of the modern agricultural industrial system of Guangdong Province.