The Coconut Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences has made new progress in mining candidate genes related to oil palm fatty acids through candidate gene association analysis. In this study, 52 genes related to fatty acid metabolism of oil palm were found through GO annotation of oil palm genome, 225 pairs of IP (Intron Polymerism) primers were designed based on intron polymorphism, and 13 IP markers were revealed to be significantly related to changes in fatty acid content based on association analysis of candidate genes. The development of these IP markers will contribute to the genetic improvement of fatty acid composition in oil palm.
Oil palm is an important tropical woody oil crop and biomass energy forest. The main product, palm oil, is derived from pulp (mesocarp) and mainly consists of palmitic acid and oleic acid (about 1:1). With the prominent problem of edible oil safety, unsaturated fatty acids such as oleic acid and linoleic acid have been paid more and more attention. Through the analysis of fatty acid components in the natural population of oil palm, it was found that the oleic acid content was significantly negatively correlated with palmitic acid (r=-0.53). This indicates that the decrease of palmitic acid content may promote the increase of oleic acid content, and it is feasible for palm oil to become a high-quality edible oil. In this study, through the association analysis between the intron polymorphism of related genes in the oil palm group and the phenotypic variation of fatty acid component content, the candidate genes related to fatty acids such as palmitic acid and linoleic acid were excavated, and quantitative verification was carried out in different tissues such as pericarp and kernel at different development stages. The results provide a theoretical basis for increasing oleic acid and linoleic acid content and decreasing palmitic acid content in oil palm breeding in the future.
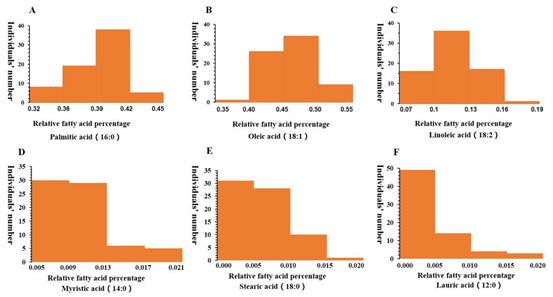
Distribution frequency of fatty acids in peel of 70 oil palm individuals
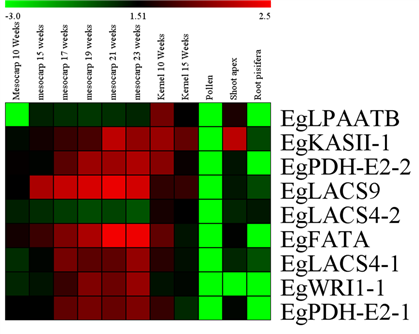
Heat map of candidate gene expression in different tissues of oil palm
The relevant research results were published in the botanical journal Frontiers in Plant Science with the research paper entitled "Development of Intron Polymerism Markers and Their Association With Fat Acid Component Variation in Oil Palm" as the first author of the paper, and researcher Xiao Yong as the corresponding author. The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.