Recently, the Haikou Experimental Station of CATAS has made new progress in identifying the involvement of Passiflora lipoxygenase (PeLOX) gene family in fruit ripening and ester formation. This research achievement describes the expression pattern of Passiflora lipoxygenase gene family in the process of abiotic stress induction and fruit ripening, and analyzes the tissue specific expression characteristics of members of this family in various organs of Passiflora, The biological evidence of one member PeLOX4 participating in fruit ripening and ester formation was obtained. This discovery laid a foundation for the functional study of Passiflora LOX.
Passiflora edulis is popular among consumers because of its rich aroma and nutritional value. Several studies have shown that esters are the main components of passionflower volatile aroma, and lipoxygenase (LOX), as the first key enzyme upstream of esters, may play an important role in the formation of passionflower aroma.
The research team screened 12 Passiflora LOX (PeLOX) members based on the Passiflora genome database, and predicted the gene structure, evolutionary analysis and cis acting factors of the family members. The results showed that PeLOX4 may be a candidate gene involved in fruit ripening and the formation of volatile aromatic compounds. With the increase of fruit maturity, the expression of PeLOX4 increased, and LOX enzyme activity also increased accordingly, thus promoting the synthesis of volatile esters in fruit pulp. This discovery laid a foundation for the functional study of Passiflora LOX.
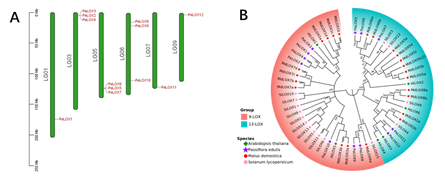
Chromosome distribution and family cluster analysis of PeLOX family.
A. PeLOX2/3/4 and PeLOX5/6/7 are connected in series and distributed on chromosomes 3 and 5;
B. The 9-LOX and 13-LOX subfamilies have 7 and 5 members, respectively.
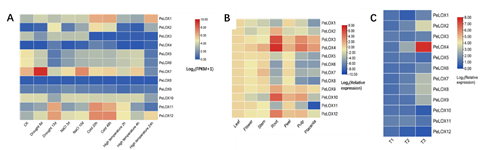
Differential expression of 12 PeLOX members under four abiotic stresses, seven tissues and three fruit development stages
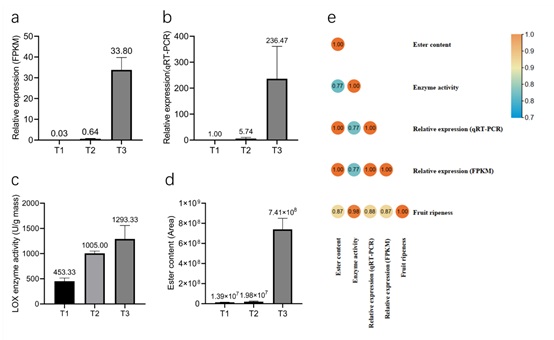
PeLOX4 relative expression, LOX enzyme activity and ester content map and correlation analysis in three different fruit development stages
The relevant research results were published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences under the title of Genome Wide Association and Expression Analysis of the Lipoxygenase Gene family in Passiflora edulis Reviewing PeLOX4 Might Be Involved in Fruit Ribbon and Ester. Huang Dongmei, Assistant Researcher of Haikou Station, Chinese Academy of Thermal Sciences, is the first author of the paper, and Song Shun, Associate Researcher of , CATAS/Sanya Research Institute and Yazhou Bay Seed Laboratory, is the corresponding author. This research has been supported by Hainan Natural Science Foundation, Yazhou Science and Technology City Elite Talent Project and National Natural Science Foundation of China.