Recently, the Leisure Agriculture Research Laboratory of the South Subtropical Crops Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences has made new progress in the field of modified pectin based new adsorbent materials. The research systematically and comprehensively elaborated the application scenario and mechanism of the new pectin based adsorbent material from the aspects of the synthesis of the modified pectin based adsorbent material, the analysis of the physical and chemical properties, the adsorption effect of heavy metal lead and the adsorption mechanism. The research results provide a new idea for the comprehensive and efficient utilization of pectin resources, and also provide theoretical support for the development and application of green, new and high adsorption performance modified pectin based adsorbent.
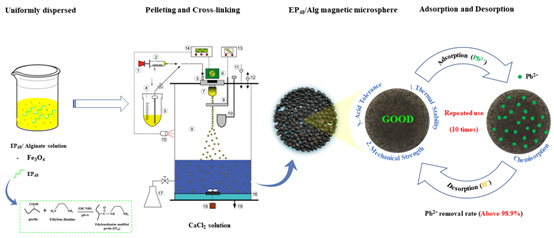
Synthesis of Modified Pectin/Sodium Alginate/Ferric Oxide Composite Microspheres and Schematic Diagram of Adsorption of Lead Ion
The wastewater from industrial production contains many heavy metals, which will be enriched in organisms and enter the human body through the food chain, posing a serious threat to the ecosystem and public health. The heavy metal lead is widely used in industrial production. It is one of the elements that cause the most serious pollution and harm the human body. It is very harmful and destructive. In recent years, biosorption, as a new heavy metal treatment method, has attracted much attention of researchers due to its wide adaptability, high selectivity, strong operability and good tolerance. Pectin is rich in resources, green and efficient, and is not easy to produce secondary pollution. As a potential biosorption material, it has good adsorption capacity for heavy metals, but its wide application is limited due to its low mechanical strength, difficult separation, difficult reuse and other shortcomings. On the basis of previous research, the research team prepared ethylenediamine modified pectin with amidation degree of 48%, compounded it with sodium alginate, embedded nano ferric oxide, used divalent calcium ion as cross-linking agent, and synthesized a new type of modified pectin based magnetic microsphere with microcapsule granulator. The results showed that the addition of sodium alginate/ferric oxide improved the thermal stability, mechanical strength, porous adsorption and acid resistance of the microspheres, making the microspheres more suitable for wastewater treatment. The maximum adsorption capacity of the modified pectin based magnetic microspheres for lead ion was 175.19 mg/g, and the removal rate remained above 98.9% after 10 adsorption desorption cycles. The microspheres can be easily separated from the solution by using an external magnetic field. These results indicate that the modified pectin based magnetic microspheres are a kind of green and renewable biosorbent with broad application prospects, which can be used to remove lead ions from wastewater. In addition, the study also preliminarily explored the adsorption mechanism of the modified pectin based magnetic microspheres for heavy metals, and found that the combination of ion exchange, metal coordination and physical adsorption was the main reason for the good water purification and adsorption performance of the modified pectin based magnetic microspheres.
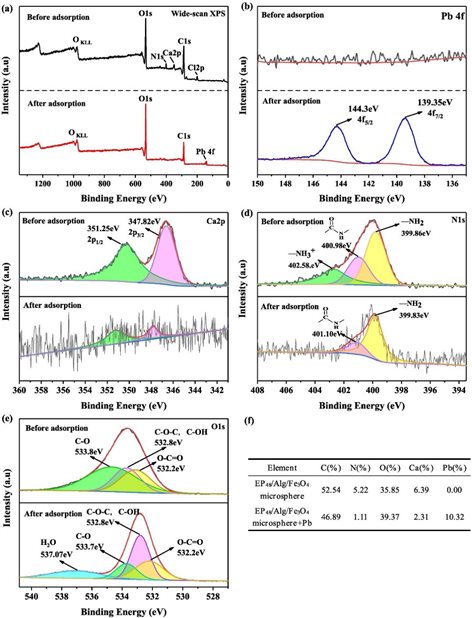
Study on the Adsorption Mechanism of Modified Pectin/Sodium Alginate/Ferric Oxide Composite Microspheres for Lead Io
This research achievement was published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules under the title of "Preparation of ethylene modified particle/originate/Fe3O4 microsphere and its effective Pb2+adsorption properties". Li Ya, a research intern of the South Subtropical Crops Research Institute of CATAS, is the first author of the paper, and Du Liqing, a researcher, is the corresponding author of the paper. The research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province (320QN320), Guangdong Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System Innovation Team Construction Project (2022KJ116) and other projects.