近日,林学国际顶级期刊《Tree physiology》在线发表了两篇我院“橡胶树等主要热带作物功能基因组学研究”创新团队资助的两篇研究论文。论文利用天然橡胶基因组数据,系统阐述了橡胶树相关基因转录水平的调控应答机制。
“Characterization of the rubber tree metallothionein family reveals a role in mitigating the effects of reactive oxygen species associated with physiological stress” (共同第一作者为黄亚成博士生、方永军和龙翔宇副研究员,通讯作者为唐朝荣研究员)。该文章初步揭示并阐述金属硫蛋白家族基因参与橡胶树生物与非生物胁迫,特别是在乳管活性氧平衡调节过程中发挥重要作用,参与了橡胶树的胶乳再生。
Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals an early gene expression profile that contributes to cold resistance in Hevea brasiliensis (the Para rubber tree)(第一兼通讯作者为橡胶研究所程汉研究员)。该论文揭示了橡胶树在低温胁迫初期的信号应答情况,解释了造成橡胶树对低温敏感、以及不同品种抗寒力差异的原因。
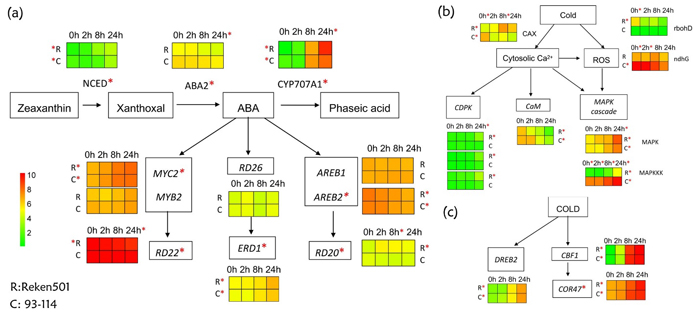
(a) ABA依赖的低温信号途径应答情况;(b) 钙离子流、ROS等早期信号分子代谢和调控基因应答情况;(c). ABA非依赖的低温信号途径基因应答情况。
本文链接:
1.Characterization of the rubber tree ... http://xueshu.baidu.com/s?wd=paperuri%3A%28793c69f546687b37b14eeb79a5e647d6%29&filter=sc_long_sign&tn=SE_xueshusource_2kduw22v&sc_vurl=http%3A%2F%2Feuropepmc.org%2Fabstract%2FMED%2F29425342&ie=utf-8&sc_us=16796685159822590617
2.Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals an early gene expression profile that contributes to cold resistance in Hevea brasiliensis (the Para rubber tree)https://academic.oup.com/treephys/advance-article/doi/10.1093/treephys/tpy014/4883210







